Understanding Female Pattern Hair Loss: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Hair isn’t just confined to the scalp; it graces various parts of the body, including the eyes, nose, and lips. However, among postmenopausal women, issues like hair thinning or bald spots are common, drawing attention to the phenomenon known as female pattern hair loss. This article aims to delve into the intricacies of female pattern baldness, examining its causes, symptoms, and available treatments.
Deciphering Female Pattern Hair Loss
The growth of hair follows a cyclical process, encompassing stages of growth, transition, and resting. Female pattern hair loss, scientifically termed androgenic alopecia, involves sudden and severe hair loss, often commencing with gradual thinning along the part line. It’s vital to understand that losing between 50 to 100 hairs daily is considered normal, reflecting the natural equilibrium of hair growth and shedding. However, when this balance is disrupted, surpassing the rate of new hair growth, symptoms of hair loss become apparent.
Varieties of Hair Loss in Women
Female hair loss presents itself in various forms, including:
- Androgenetic Alopecia: This is the most prevalent type, often hereditary but manageable through medical intervention.
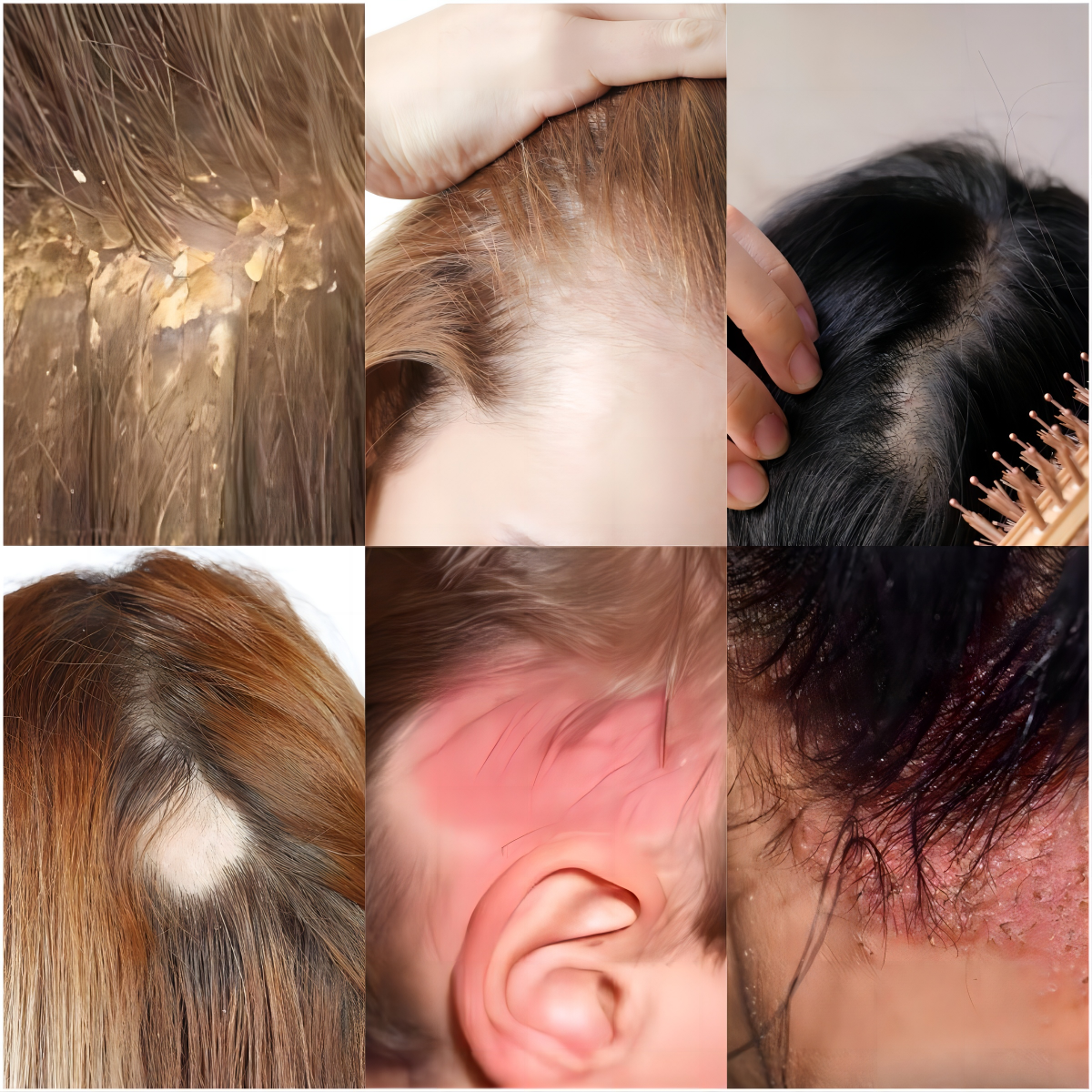
- Telogen Effluvium: Hair growth temporarily halts, typically due to physiological stressors.

- Anagen Effluvium: Rapid hair loss induced by medical treatments such as chemotherapy.

- Alopecia Areata: An autoimmune condition resulting in patchy hair loss due to immune system attacks on hair follicles.

- Tinea Capitis: Also known as “ringworm of the scalp,” this fungal infection causes hair loss in patches, with the affected area appearing scaly and itchy.

- Cicatricial Alopecia: Commonly referred to as scarring alopecia, this condition involves inflammation of the scalp, leading to irreversible damage to hair follicles.

Symptoms of Female Pattern Hair Loss
There isn’t a single symptom of female pattern hair loss; it can manifest in various ways, depending on the underlying cause. Severe hair loss doesn’t just affect the scalp; it can impact the entire body. Common symptoms include:
- Thinning hair on the top of the head, often accompanied by a receding hairline.
- Patchy baldness, not limited to the scalp but also affecting eyebrows and beard.
- Loosening of hair roots, noticeable during washing or brushing.
- Complete baldness, which can be a side effect of certain medical treatments like chemotherapy.
Main Causes of Hair Loss in Women
Several factors contribute to hair loss in women, including:
- Genetic Inheritance: Hereditary factors play a significant role, with genetic hair loss often becoming noticeable after the age of 40.

- Hormonal Imbalance: Fluctuations in hormone levels, particularly androgens and estrogen, can weaken hair follicles, leading to increased hair loss.

- Abrupt Dieting: Dramatic weight loss can trigger sudden hair loss due to nutrient deficiencies and the body’s self-protection mechanisms.

- Thyroid Problems: Disorders like hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism can disrupt hormone levels, resulting in hair loss.
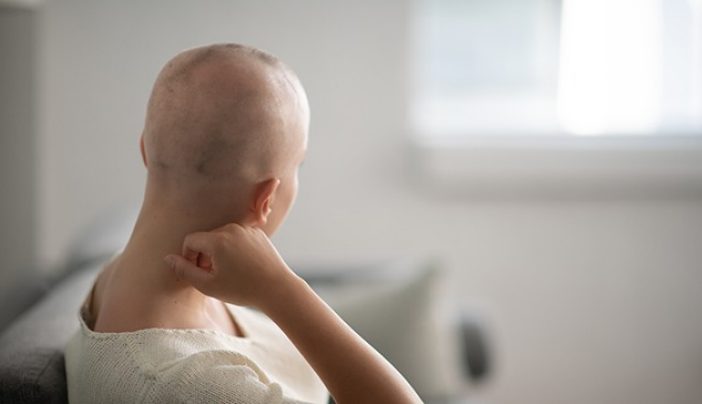
- Certain Medications: Some medications, such as oral contraceptives, anti-inflammatory drugs, and chemotherapy agents, can cause hair loss as a side effect.

- Intense Stress: Physical and emotional stressors can lead to acute hair loss, often triggered by traumatic events or chronic stress.
- Postpartum Changes: Hormonal fluctuations post-pregnancy can cause temporary hair loss, which typically resolves with time and proper care.

Treatment Options for Female Pattern Hair Loss
Addressing female pattern hair loss involves a multi-faceted approach, including:
-
Medications: FDA-approved medications like minoxidil and finasteride are commonly prescribed to stimulate hair regrowth and prevent further loss.
-
Hormonal Therapy: Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) can help balance hormone levels, particularly in postmenopausal women experiencing hair loss due to hormonal imbalances.
-
Nutritional Supplements: Supplements containing biotin, iron, zinc, and other essential nutrients can promote hair health and growth.
-
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: This innovative treatment involves injecting platelet-rich plasma derived from the patient’s blood into the scalp to stimulate hair growth.
-
Hair Transplant Surgery: In cases of severe or irreversible hair loss, surgical procedures like follicular unit transplantation (FUT) or follicular unit extraction (FUE) can restore a fuller head of hair.
Conclusion
Female pattern hair loss can have profound psychological and emotional effects, impacting self-esteem and quality of life. However, with advances in medical science and a better understanding of the underlying causes, effective treatments are available to address this condition. It’s essential for individuals experiencing hair loss to consult with healthcare professionals to determine the most suitable course of action tailored to their specific needs.




