Introduction to Hair Thinning
Dealing with thinning hair or hair loss can be a daunting experience, impacting one’s self-esteem and confidence. But fret not, as there are effective treatments available to combat this issue.
*Explore more: >*
Moreover, wearing a wig can serve as a confidence booster throughout this journey. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the causes of thinning hair. By understanding these factors, you can make informed decisions to regain control over your hair’s health.
*Related: >*
** >**
Key Points to Consider
-
Selecting the appropriate treatment tailored to the underlying cause of thinning hair is crucial.
-
Medical interventions, including prescription medications and advanced surgeries, can deter hair thinning effectively.
-
Lifestyle modifications and non-medical interventions also play a pivotal role in preventing thinning hair.
Understanding Thinning Hair and Its Causes

Recognizing the root causes of hair loss is imperative for devising an effective treatment plan. Various factors contribute to hair loss, such as genetic predisposition, hormonal imbalances, certain medications, and medical conditions. Among age-related hair loss conditions, female pattern hair loss and alopecia are common.
Diagnosing hair loss entails a thorough physical examination and gathering information about one’s diet, hair care routine, medical history, and family history. Once the underlying cause is identified, appropriate treatment can be initiated to halt further hair loss and stimulate regrowth.
Identifying Different Types of Hair Loss
Female pattern hair loss (androgenic alopecia) and female-pattern baldness are predominant types of hair loss. The former is often linked to genetic or age-related hormonal changes, posing challenges in hair regeneration.
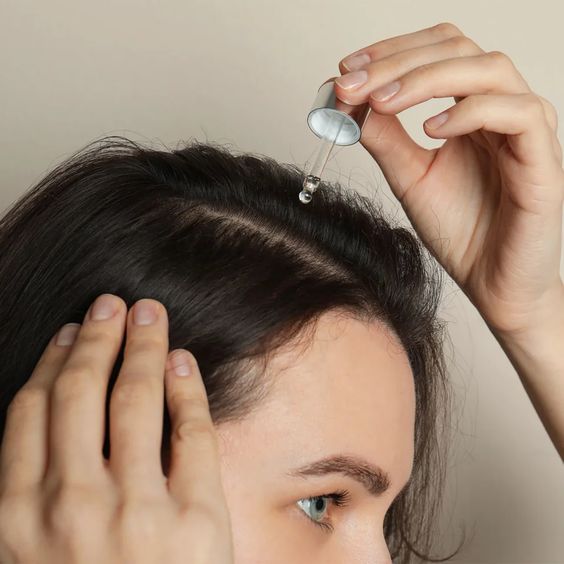

Distinguishing between gradual hair thinning and sudden hair loss aids in selecting suitable treatment approaches.
FPHL and Genetic Factors
Female pattern hair loss (FPHL) is prevalent among women, characterized by non-scarring and non-inflammatory hair thinning. It typically manifests as frontal hairline retention accompanied by gradual hair loss in the middle and frontal scalp regions.
Understanding the significance of family history in hair loss is paramount, as it highlights the hereditary nature of the condition. Recognizing the role of genetics and familial predisposition enables individuals to seek appropriate treatment.
Factors Contributing to Hair Loss in Women
Hereditary factors play a significant role in hair loss, with androgenetic alopecia being the most common genetic condition. Women experiencing this condition may notice a widening of the hair parting in their 40s or 50s.
Inflammatory scalp conditions, such as eczema and psoriasis, predispose individuals to hair loss. Proper treatment and medication are imperative to address hair loss in such cases.
Other contributing factors include excessive use of harsh hair care products, heat damage from styling tools, nutritional deficiencies, poor sleep quality, and underlying medical conditions.
Medical Interventions for Female Hair Loss
Medical treatments offer viable solutions to slow down or reverse hair thinning. These may include over-the-counter and prescription medications, as well as hair transplant procedures. While some treatments focus on reducing hair loss, others stimulate hair regrowth.
Surgical interventions, such as hair transplant surgery, provide an alternative for treating alopecia. Prescription medications like minoxidil and finasteride are commonly prescribed for hair loss, demonstrating efficacy in promoting hair regrowth.
Advanced procedures, including hair transplantation, involve transplanting hair from donor areas to areas experiencing hair loss. Although these procedures offer lasting results, potential risks such as infection and scarring should be considered.
Non-Medical Approaches to Enhance Hair Growth

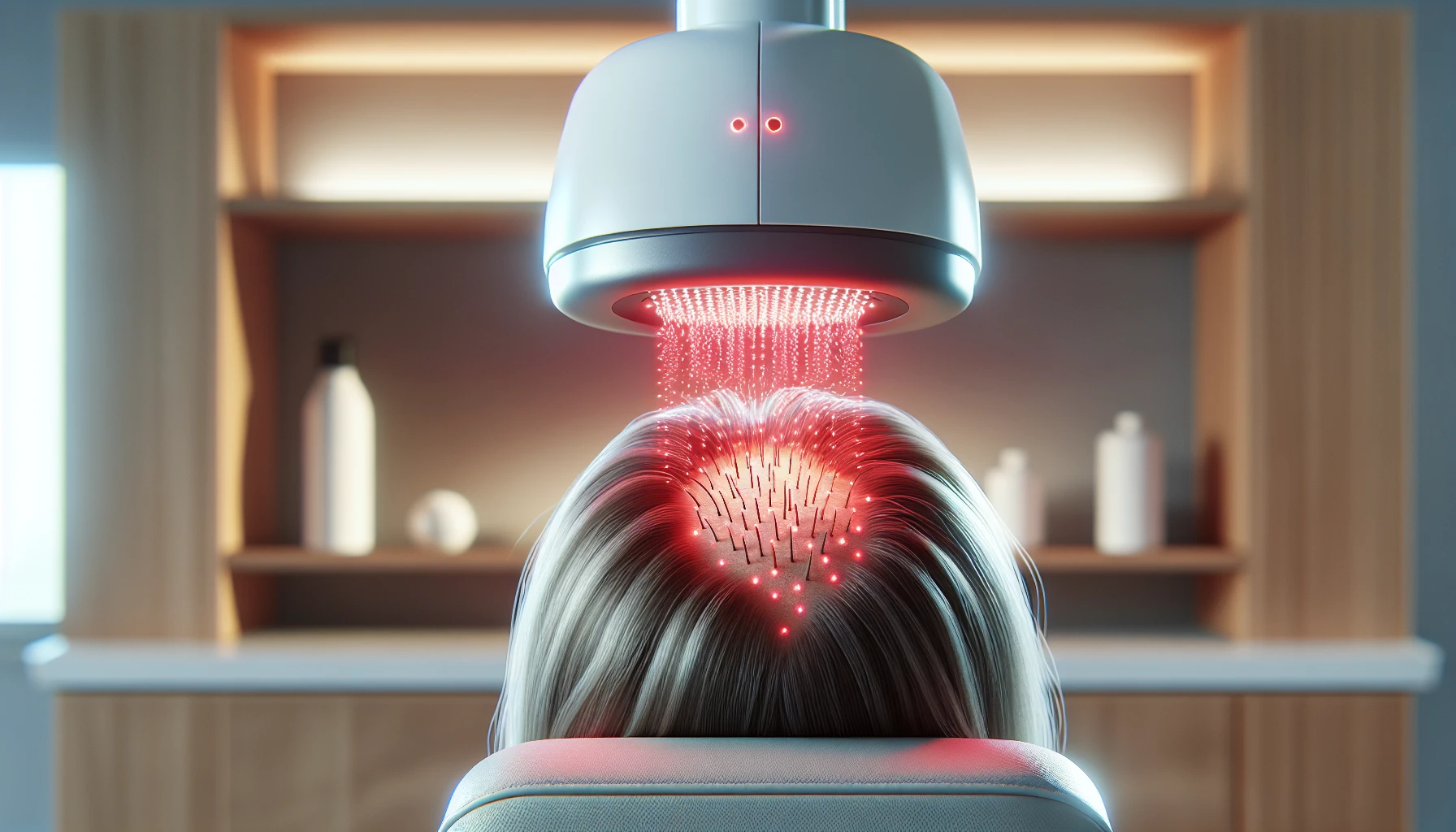
In addition to medical treatments, non-medical interventions like low-intensity laser therapy and natural remedies can promote hair growth and increase hair density. These options are suitable for individuals seeking less invasive solutions for hair loss.
►>Low-Intensity Laser Therapy
Low-intensity laser therapy (LLLT) is an FDA-approved treatment for hereditary hair loss, utilizing low-power lasers or LEDs to stimulate hair growth. It enhances blood flow to the hair follicles, facilitating nutrient delivery and cell activity, thereby fostering thicker and healthier hair growth.
Research indicates LLLT’s efficacy in stimulating hair growth in conditions such as chemotherapy-induced hair loss and alopecia areata.
►>Natural Remedies and Supplements
Natural remedies like saw palmetto and biotin, along with supplements, show promise in promoting hair regeneration. Research suggests that green tea polyphenols may also serve as a potential natural treatment for hair loss.
Benefits of saw palmetto for hair growth include preventing hair loss, enhancing hair quality, and increasing hair density.
In conclusion, understanding the causes and available treatments for hair loss empowers individuals to address this concern effectively, restoring confidence and promoting overall well-being.
Understanding Saw Palmetto for Hair Health

Saw palmetto, known for its potential in addressing hair loss, offers various benefits, including:
- Reduction of scalp inflammation
- Prevention of hair loss
- Stimulation of follicle growth
- Inhibition of DHT, a hormone responsible for hair loss in women
- Increased hair density
The recommended daily dosage of saw palmetto for hair loss ranges from 160 to 320 mg.
Adopting Lifestyle Changes to Combat Hair Loss

Implementing lifestyle adjustments is instrumental in curbing further hair loss and maintaining hair health. Embracing a balanced diet, proper hydration, and gentle hair care routines significantly enhance hair condition and reduce the risk of hair loss.
►>Optimize Resting Habits
Irregular sleep patterns, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption can impact hair health. Prioritize adequate rest, as the body’s hair growth mechanisms are particularly active during sleep. Utilize sleeping caps to improve sleep quality and safeguard hair health.

Nutritional Strategies for Healthy Hair
Ensuring a well-rounded diet rich in essential nutrients and staying hydrated is vital for optimal hair health. Foods abundant in zinc, vitamin C, omega fatty acids, protein, B vitamins, vitamin D, and iron support hair growth and vitality. Combining biotin with zinc has shown effectiveness in maintaining hair, skin, and muscle health.
Selecting the Right Wig

Choosing a suitable wig is paramount, especially for individuals experiencing partial or complete hair loss. Wigs offer a cost-effective and versatile solution, catering to diverse preferences and needs.
Maintaining a Positive Mindset
Fostering a positive outlook is crucial in managing hair loss. Excessive stress can trigger hair follicles to enter a resting phase, leading to hair shedding. Additionally, stress-induced alopecia areata may occur, prompting the immune system to attack hair follicles.
Embracing Gentle Hair Care Practices

Adopting gentle hair care habits, such as avoiding harsh chemicals and minimizing heat styling, preserves hair health and minimizes damage. Incorporate regular trims, air drying, and protective hairstyles into your routine to promote hair strength and vitality.
Seeking Professional Guidance

Knowing when to seek professional assistance is pivotal in addressing hair loss effectively. Consulting a primary care physician or dermatologist enables thorough evaluation of potential causes and discussion of treatment options. Diagnostic tests may be conducted to pinpoint underlying factors contributing to hair loss.
Preparing for Medical Evaluation
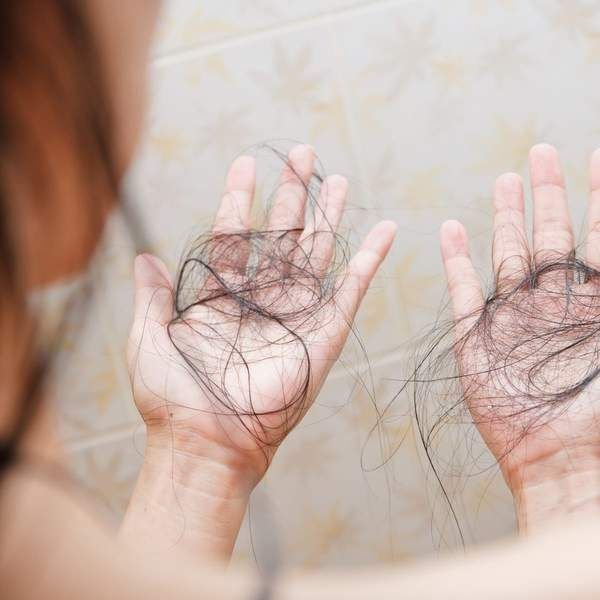

Before scheduling a hair loss treatment appointment, provide comprehensive details about your lifestyle, medical history, and recent stressors to your healthcare provider. Relevant laboratory tests may aid in identifying underlying issues contributing to hair loss.
In Conclusion
Hair loss can be managed through a multifaceted approach, encompassing medical interventions, lifestyle modifications, and gentle hair care practices. Understanding the root causes of hair loss and seeking professional guidance when necessary empower individuals to regain control over their hair’s health. With perseverance and tailored strategies, achieving healthier, revitalized hair becomes attainable.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which Treatment is Best for Hair Loss?
Medical experts recommend minoxidil as a top treatment for hair loss, enhancing blood circulation to follicles and facilitating nutrient absorption. Finasteride is another effective option for hereditary hair loss.
How Can Hair Loss be Prevented?
Preventive measures include smoking cessation, sun protection, nutrient-rich diets, and scalp care routines. Additionally, scalp massages, essential oils, and specialized shampoos may aid in hair loss prevention.
Is Hair Loss Reversible?
With appropriate diagnosis and treatment, hair loss can be reversed in some cases, allowing for regrowth and restoration of hair health.
What Causes Hair Loss?
Androgenetic alopecia, a genetic condition, is a common cause of hair loss in women. Other factors, such as medication, hormonal changes, and aging, may also contribute to hair loss.
What are the Benefits of Choosing Your Own Wig?
Selecting a suitable wig ensures comfort, aesthetics, and improved self-esteem. Wigs cater to individual preferences and offer natural-looking solutions for hair loss concerns.




